Reports Table with Pagination & CSV Download - Part 1
Implementing Reports Table with SWR and CSV Download using Asynchronous API and Node.js Worker
Hi fellow readers 👋🏻,
In my previous post, we discussed our Hackathon and the CL Survey MVP. This time, we'll delve deeper into the reports table and CSV download implementation. Let's get started!
Reports Table Implementation
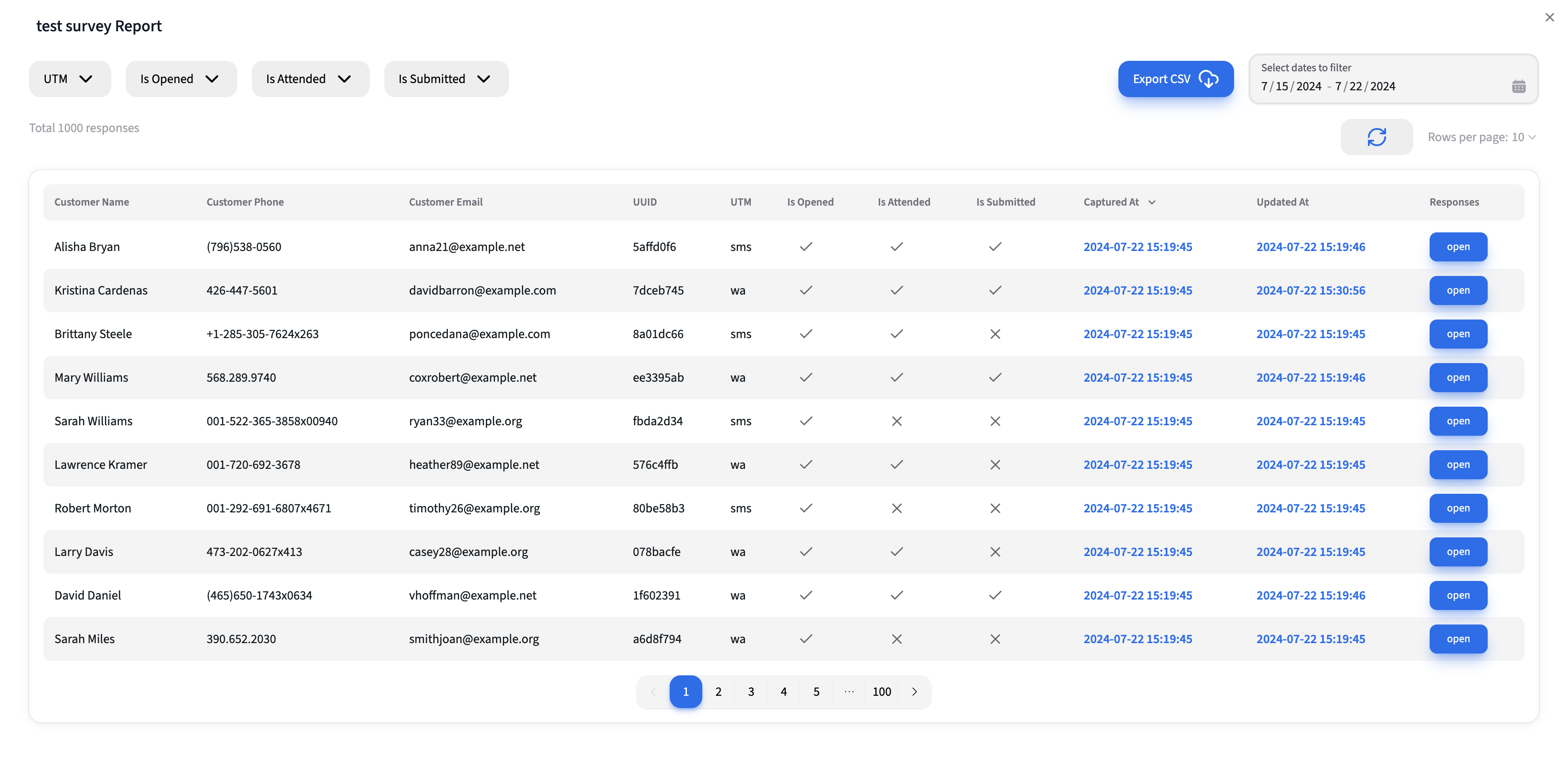
Table Fields
- Customer Information: Name, Phone, Email
- UUID
- Unique identifier mapped to the customer during survey request creation.
- UTM
- Source identifier (e.g., SMS, WhatsApp) appended to the survey URL.
- Survey Flags
- Is Opened: Indicates if the customer opened the survey.
- Is Attended: Indicates if the customer attended any questions.
- Is Submitted: Indicates if the customer submitted the survey.
- Timestamps
- Captured At: Timestamp of when the survey was captured.
- Updated At: Timestamp of the last update.
- Responses
- Clicking the "open" button reveals a modal with all survey responses.
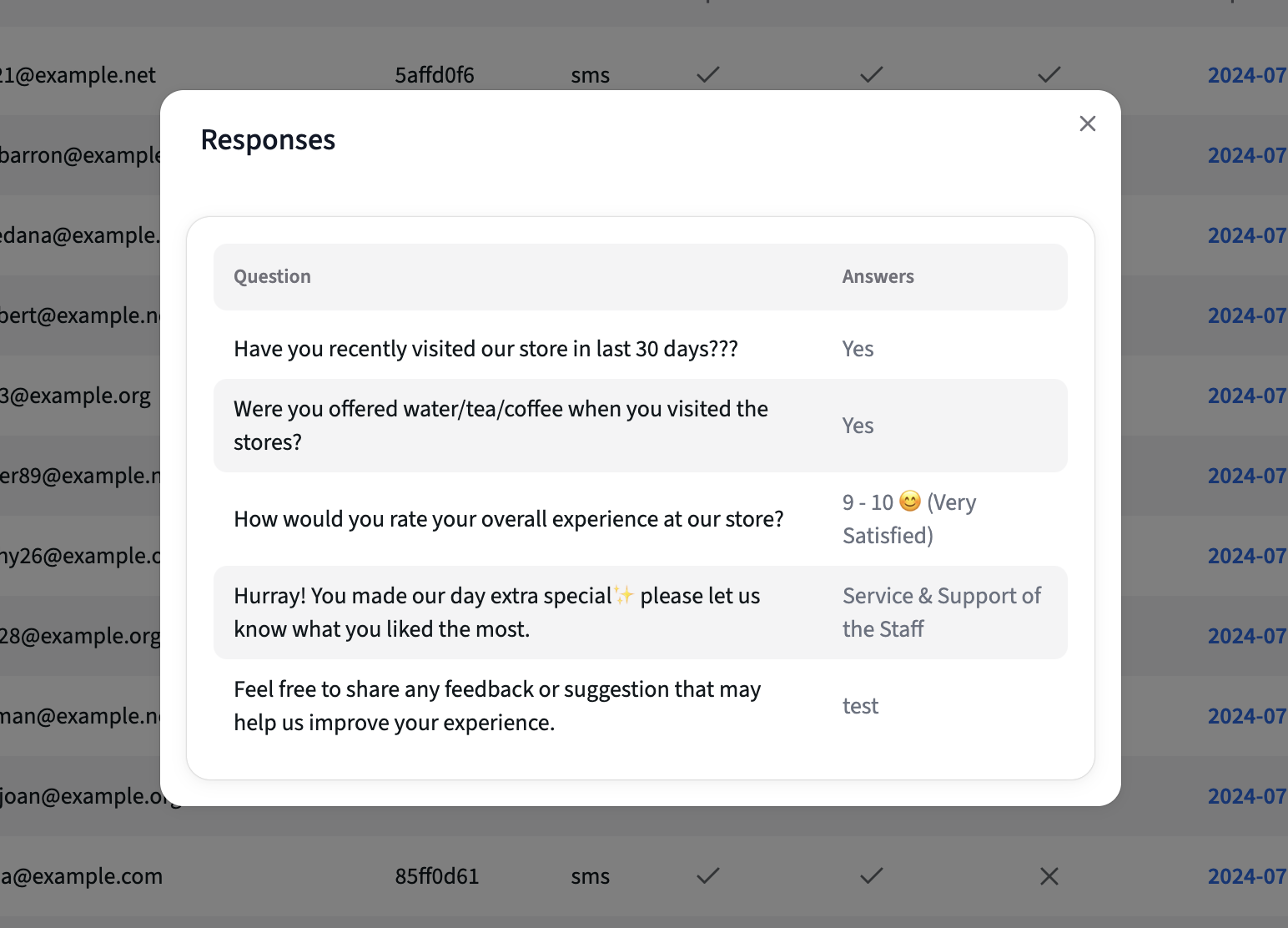
- Pagination: Allows toggling between different pages of responses.
- Filters: Multi-select dropdown filters and date filter for refining the data.
- Total Responses: Displays the total number of responses.
- Refresh Button: Fetches real-time updates.
- Rows per page: Allows to select rows per page. Example: 10,20,50 etc,.
Introduction to SWR
Before diving into the implementation details, let's briefly discuss SWR, a powerful library for data fetching in React applications.
SWR stands for "Stale-While-Revalidate." It's a React Hooks library created by Vercel that provides a simple and efficient way to fetch, cache, and revalidate data in real-time. SWR aims to keep your UI fast and reactive by ensuring that the data is always up-to-date without compromising performance.
Introduction to Axios Cache Interceptor
In addition to using SWR for data fetching, another powerful tool to enhance the performance of your React application is Axios combined with a Axios cache interceptor.
Axios is a popular HTTP client library for making requests to APIs. It’s widely used in modern web applications due to its simplicity and ease of use.
An Axios cache interceptor allows you to cache responses to repeated requests. This means that if the same request is made multiple times, the cached response can be returned instead of hitting the server again. This can lead to faster response times and a more efficient application.
Setting up Axios with Cache Interceptor
- Install Axios and Axios Cache Interceptor
yarn add axios axios-cache-interceptor
- Configure Axios with Cache Interceptor
import axios from 'axios';
import { buildWebStorage, setupCache } from 'axios-cache-interceptor';
const instance = axios.create({
baseURL: '/api',
});
// Set up the cache
const coreInstance = setupCache(instance, {
storage: buildWebStorage('local'), // Using localStorage for caching
maxAge: 15 * 60 * 1000, // Setting up ttl for 15 minutes
exclude: { query: false } // Optionally exclude query parameters from caching
});
export default coreInstance;
In this code:
- We import axios and axios-cache-interceptor.
- The setupCache method from axios-cache-interceptor is used to set up the cache. Here, buildWebStorage is used to store the cache in localStorage, but you can also use other storage options like sessionStorage or custom storage solutions.
- The maxAge option sets the cache duration to 15 minutes.
- The exclude option can be used to exclude certain types of requests from being cached.
SWR Fetcher Function
To use SWR for data fetching, we define a fetcher function that leverages our cached Axios instance. This function will handle API requests and ensure the responses are cached appropriately.
const fetcher = (url: string) =>
coreInstance
.get(url, {
id: \`report-\${surveyId}-page-\${page}-\${url}\`,
})
.then(res => res.data);
Generating the URL with useMemo
To ensure our data fetching is efficient, we use useMemo to generate the URL based on dependencies. This ensures that the URL is only recalculated when one of the dependencies changes, avoiding unnecessary recomputations.
const url = useMemo(
() =>
\`/reports?surveyId=\${surveyId}&from=\${from}&to=\${to}&page=\${page}&count=\${rowsPerPage}\${isOpened}\${isAttended}\${isSubmitted}\${utm}\${sort}\`,
[
from,
isAttended,
isOpened,
isSubmitted,
page,
rowsPerPage,
sort,
surveyId,
to,
utm,
],
);
Using SWR for Data Fetching
Finally, we use SWR to fetch data with the generated URL and fetcher function. SWR provides an elegant way to handle data fetching, caching, and revalidation.
const {
data,
isLoading,
mutate: mutateData,
}: {
data: IReports;
isLoading: boolean;
mutate: MutatorCallback;
} = useSWR(surveyId ? url : null, fetcher, {
revalidateOnFocus: false,
revalidateOnReconnect: false,
refreshWhenOffline: false,
refreshWhenHidden: false,
refreshInterval: 0,
});
Explanation of SWR Options
- revalidateOnFocus: false: Disable revalidation when the window is refocused
- revalidateOnReconnect: false: Disable revalidation when the network is reconnected
- refreshWhenOffline: false: Disable revalidation when the browser is offline
- refreshWhenHidden: false: Disable automatic revalidation when the window is hidden.
- refreshInterval: 0: Disable periodic revalidation.
Putting It All Together
Here's how everything fits together in a React component:
import { axiosInstance } from '@/utils/axios';
import { Key } from '@react-types/shared';
import { useMemo, useState } from 'react';
import useSWR, { MutatorCallback } from 'swr';
export default function SurveyDataTable() {
const [page, setPage] = useState(1);
const todayDate = today(getLocalTimeZone());
const sevenDaysAgoDate = todayDate.subtract({ days: 7 });
const [startValue, setStartValue] = useState(parseDate(sevenDaysAgoDate.toString()));
const [endValue, setEndValue] = useState(parseDate(todayDate.toString()));
const [utmFilter, setUtmFilter] = useState<'all' | Iterable<Key> | undefined>('all');
const [isOpenedFilter, setIsOpenedFilter] = useState<'all' | Iterable<Key> | undefined>('all');
const [isAttendedFilter, setIsAttendedFilter] = useState<'all' | Iterable<Key> | undefined>('all');
const [isSubmittedFilter, setIsSubmittedFilter] = useState<'all' | Iterable<Key> | undefined>('all');
const [sortFilter, setSortFilter] = useState<'asc' | 'desc'>('desc');
const surveyId = useMemo(() => get('surveyId'), [get]);
const from = useMemo(() => {
return `${startValue.year}-${startValue.month}-${startValue.day}`;
}, [startValue]);
const to = useMemo(() => {
return `${endValue.year}-${endValue.month}-${endValue.day}`;
}, [endValue]);
const isOpened = useMemo(() => {
const yes = new Set(isOpenedFilter).has('yes');
const no = new Set(isOpenedFilter).has('no');
if (isOpenedFilter === 'all' || (yes && no)) return '';
return yes ? '&isOpened=1' : '&isOpened=0';
}, [isOpenedFilter]);
const isAttended = useMemo(() => {
const yes = new Set(isAttendedFilter).has('yes');
const no = new Set(isAttendedFilter).has('no');
if (isAttendedFilter === 'all' || (yes && no)) return '';
return yes ? '&isAttended=1' : '&isAttended=0';
}, [isAttendedFilter]);
const isSubmitted = useMemo(() => {
const yes = new Set(isSubmittedFilter).has('yes');
const no = new Set(isSubmittedFilter).has('no');
if (isSubmittedFilter === 'all' || (yes && no)) return '';
return yes ? '&isSubmitted=1' : '&isSubmitted=0';
}, [isSubmittedFilter]);
const utm = useMemo(() => {
const wa = new Set(utmFilter).has('wa');
const sms = new Set(utmFilter).has('sms');
if (utmFilter === 'all' || (wa && sms)) return '';
return wa ? '&utm=wa' : '&utm=sms';
}, [utmFilter]);
const sort = useMemo(() => {
return sortFilter ? `&sort=${sortFilter}` : '';
}, [sortFilter]);
const fetcher = (url: string) =>
axiosInstance
.get(url, {
id: `report-${surveyId}-page-${page}-${url}`,
})
.then(res => res.data);
const url = useMemo(
() =>
`/reports?surveyId=${surveyId}&from=${from}&to=${to}&page=${page}&count=${rowsPerPage}${isOpened}${isAttended}${isSubmitted}${utm}${sort}`,
[
from,
isAttended,
isOpened,
isSubmitted,
page,
rowsPerPage,
sort,
surveyId,
to,
utm,
],
);
const {
data,
isLoading,
mutate: mutateData,
}: {
data: IReports;
isLoading: boolean;
mutate: MutatorCallback;
} = useSWR(surveyId ? url : null, fetcher, {
revalidateOnFocus: false,
revalidateOnReconnect: false,
refreshWhenOffline: false,
refreshWhenHidden: false,
refreshInterval: 0,
});
return (
<>
{/* Your component JSX goes here */}
</>
);
}
Explanation
First, we are setting up states for pagination and filters using the useState hook then using useMemo, we compute values based on the states and filters. This ensures that values are recalculated only when their dependencies change and we construct the URL dynamically based on the memoized values and use useSWR for data fetching. The fetcher function uses Axios to make the API request, and useSWR handles caching and revalidation.
In this component, we maintain states for pagination and various filters. When any state changes, the memoized values are recalculated, updating the URL. The useSWR hook observes the URL and triggers a new API call whenever it changes. By using an Axios instance with a cache interceptor, we ensure that data is fetched from the server only on the first request. Subsequent requests retrieve data from the cache, enhancing performance and reducing server load.
This approach leverages React hooks and SWR’s powerful features to create an efficient, dynamic data table component. The use of memoization and caching ensures optimal performance, making the user experience smooth and responsive.
Wrapping Up 🎉
Voila! 🎉 We've covered setting up a dynamic reports table with pagination, using SWR and Axios with a cache interceptor to ensure efficient and responsive data fetching. The setup ensures that our app remains snappy and doesn't unnecessarily hit our servers with repeated requests.
In the next part, we'll dive into the fun stuff - implementing the CSV download feature using an asynchronous API and Node.js worker thread. We'll see how to handle large datasets without freezing our UI and provide a seamless download experience for users.
Stay tuned and get ready to geek out! 🤓🚀
Until next time, happy coding! ✌️